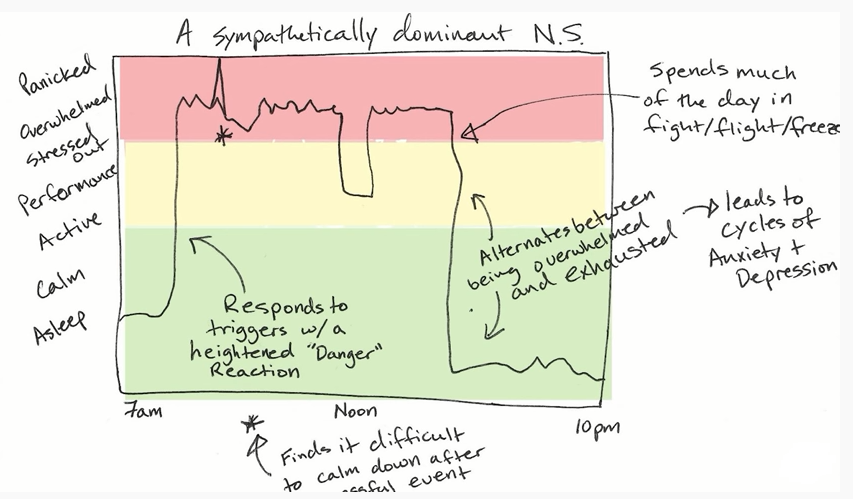
Science behind the Trauma
As you learn about a danger or perceived danger to your survival, the Amygdala in your brain alerts the Hypothalamus about the danger based on the basic instinctual program for survival. This will put your system into survival (fight/flight/freeze) mode, which will cause the release of Cortisol and Adrenaline. These hormones prepare your body to deal with the impending perceived/real danger. When this situation persists for a longer period, the nervous energy which is making all these activities happen gets stuck in it, rather than going down to baseline operation; ie, when humans live in a safe environment. This stuck energy in the nervous system causes havoc in the day-to-day living of human beings, resulting in the dis-regulation of the nervous system. This situation is known as the person living in a state of Trauma.
The situations that can cause Trauma
Children exposed to violence or toxic relationships among parents.
Not received secure attachment in early childhood at least with one adult care giver.
Mother going through traumatic experiences during the pregnancy period.
Sexual or Verbal abuse before the age of seven.
Unprofessional work environment where individual dignity and personal space and time is not respected and unrealistic expectations are imposed.
Symptoms of a person living in a state of Trauma
- Trauma-induced high cortisol level in the body affects the cells, body tissues, and hormonal balance such as the thyroid.
- You are susceptible to stressful situations, and hence you may get triggered too quickly compared to other people who are not suffering from any kind of trauma in their life.
- It can cause cardiovascular issues and kidney issues.
- Vulnerable to addiction
- Premature aging
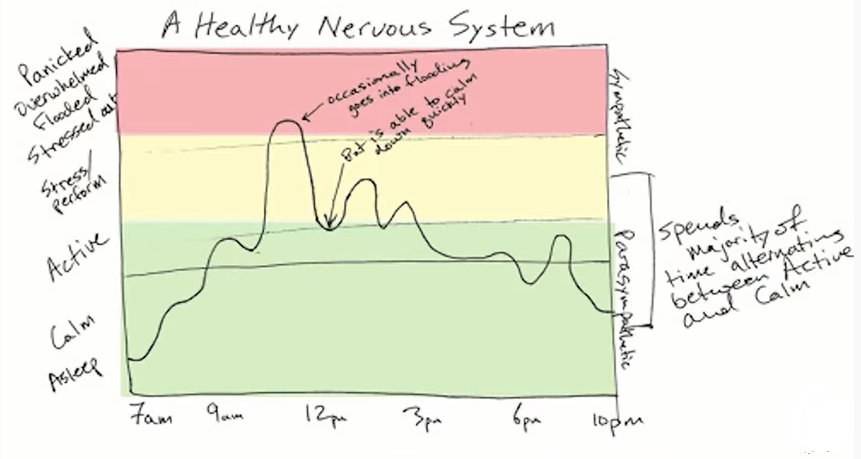
Effects of Trauma in individual’s life
- Due to epigenetic effects, intergenerational transmission is also possible.